
Family • Moraceae
Botgo
Ficus caulocarpa (Miq.) Miq.
WHITE FIG
Da ye chi rong
| Scientific names | Common names |
| Ficus caulocarpa (Miq.) Miq. | Balete (Tag., Ibn., Bon., P. Bis.) |
| Ficus caulocarpa var. dasycarpa Corner | Botgo (Bik.) |
| Ficus infectoria var. caulocarpa (Miq.) King | Bubulung (Sbl.) |
| Ficus stipulosa Miq. | Dalakit (C. Bis.) |
| Ficus virens var. caulocarpa (Miq.) M.R.Almedia | Kuba (Ting.) |
| Ficus weinlandii K.Schum. | Lonok (Ilonggo) |
| Magamano (Bag.) | |
| Nonok (P. Bis.) | |
| Pasapla (Ilk.) | |
| Puspus (Ting.) | |
| Sanglau (Ilk.) | |
| White fig (Engl.) | |
| Worldwide there are over 800 species of the genus Ficus (Latin: fig) and of the more than 10 species found in the Philippines, Balete is a shared common name for six of them: (1) Ficus benjamina, salisi (2) Ficus elastica , Indian rubber tree (3) Ficus indica, baleteng-baging (4) Ficus payapa, payapa (5) Ficus retusa, marabutan, and (6) Ficus stipulosa, botgo. | |
| Ficus stipulosa is a synonym of Ficus caulocarpa (Miq.) Miq. The Plant List | |
| Ficus caulocarpa (Miq.) Miq. is an accepted name. The Plant List` | |
| White fig is a common name shared by Ficus caulocarpa and Ficus virens. | |
| Other vernacular names |
| BRUNEI: Bukit patoi. |
| CHINESE: Da ye chi rong. |
| INDIA: Pakad. |
| JAPANESE: Oo baakou. |
Updated June 2021 / September 2018 / August 2014
![]()
 |
PHOTOS / ILLUSTRATIONS |
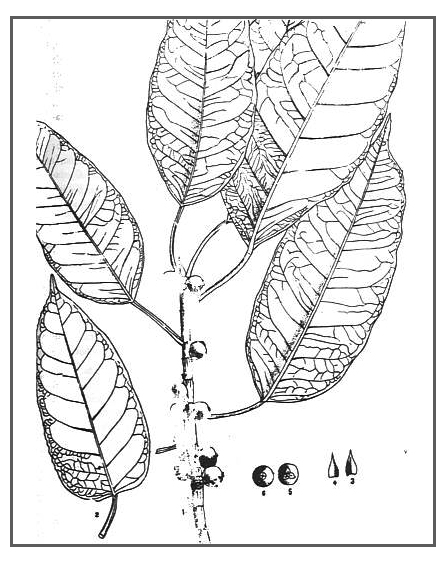
| IMAGE SOURCE: Photograph: Ficus caulocarpa / / Abaxial view of leaf / Copyright © 2018: P.B. Pelser & J.F.Barcelona / pieter.pelser@canterbury.ac.nz) [ref. DOL129003] click on image to go to source page / PhytoImages.siu.edu |
| OTHER IMAGE SOURCE: Ficus infectoria Roxb. / [Bildquelle: Kirtikar-Basu, ©1918] / Payer.de |
Additional
Sources and Suggested Readings |
• |
DOI: It is not uncommon for links on studies/sources to change. Copying and pasting the information on the search window or using the DOI (if available) will often redirect to the new link page. (Citing and Using a (DOI) Digital Object Identifier) |
• |
| Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â List of Understudied Philippine Medicinal Plants |
 |


 Distribution
Distribution