 Gen info Gen info
- Etymology: The genus name Cayratia from the Annamese vernacular name "cay-rat" meaning "a vine". The specific epithet derives from Latin words tri- meaning "three" and folium meaning "leaf", referring to the leaves bearing three leaflets.
Botany
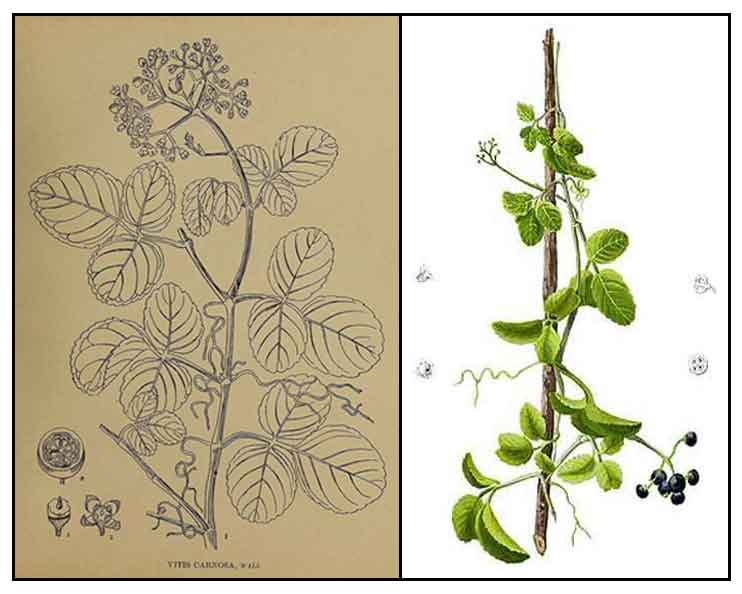
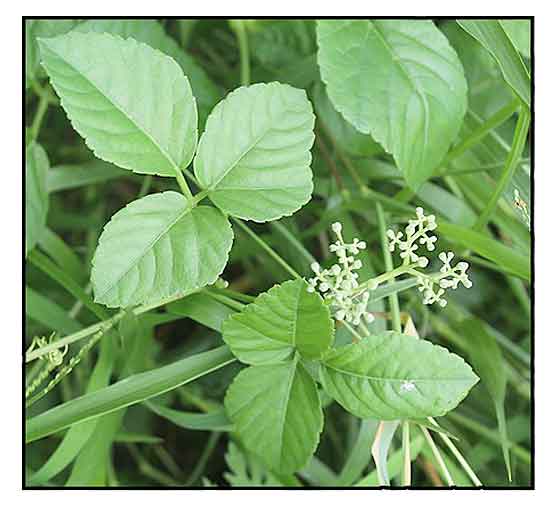
Kalit-kalit is a perennial vine, climbing by means of tendrils found opposite the leaves. Leaves are trifoliolate with petioles 2 to 3 centimeters long. Leaflets are ovate to oblong-ovate, 2 to 8 centimeters long, 1.5 to 5 centimeters wide, pointed at the tip, and coarsely toothed at the margins. Flowers are small, greenish white, borne on axillary and solitary cymes. Fruit is a berry, fleshy, juicy, dark purple or black, subglobose, and about 1 centimeter in diameter.
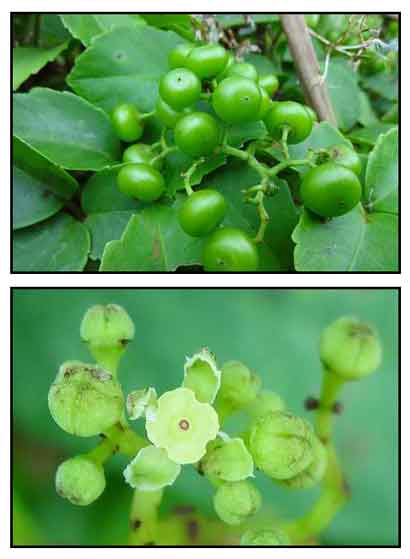 Causonis trifolia is a herbaceous climber which grows by twining around a source of support or by the use of tendrils to climb up taller objects. Leaves are spirally arranged, compound and stalked with three toothed-margined leaflets (3-foliolate). Terminal leaflet blade is drop-shaped, oblong to oval, and 5.5–7 by 3.5–4.5 cm. Lateral leaflet is oval and 3.5–5.5 by 3–4 cm. Leaf base cuneate to rounded, apex acute to acuminate. Petiole is 1- 6 cm long. Tendrils are slender and wiry. Stem is 1 - 4 mm in diameter, highly branched, hairy with pale hair. Flowering shoot is up to 2 cm across and found in the leaf axils. Fruits are smooth, disc-shaped berries, 0.5– 1.5 cm wide, and contain 2–4 triangular seeds each. Its seed is 5–6 x 4.5–5 mm. (21) Causonis trifolia is a herbaceous climber which grows by twining around a source of support or by the use of tendrils to climb up taller objects. Leaves are spirally arranged, compound and stalked with three toothed-margined leaflets (3-foliolate). Terminal leaflet blade is drop-shaped, oblong to oval, and 5.5–7 by 3.5–4.5 cm. Lateral leaflet is oval and 3.5–5.5 by 3–4 cm. Leaf base cuneate to rounded, apex acute to acuminate. Petiole is 1- 6 cm long. Tendrils are slender and wiry. Stem is 1 - 4 mm in diameter, highly branched, hairy with pale hair. Flowering shoot is up to 2 cm across and found in the leaf axils. Fruits are smooth, disc-shaped berries, 0.5– 1.5 cm wide, and contain 2–4 triangular seeds each. Its seed is 5–6 x 4.5–5 mm. (21)
Distribution
- Natuve to the Philippines.
-
Throughout the Philippines, in thickets at low altitudes.
- Also native to Andaman Is., Assam, Australia, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China, Himalaya, India, Jawa, Laos, Malaya, Maluku, Myanmar, Nepal, New Guinea, Northern Territory, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Thailand, Vietnam, etc. (13)
Constituents
- Plant yields a yellow waxy oil, carbohydrates, steroids, terpenoids, flavonoids and tannins.
- Yield kaempferol, myricetin, quercetin, triterpenes, and epifriedelanol.
- Plant leaf yields steroids, tannins, flavonoids, fatty acid, and terpenoids.
- Leaves yield stilbenes (piceid, resveratrol, viniferin, ampelopsin) and flavonoids (cyanidins).
- Stems, leaves, roots reported to yield hydrocyanic acid and delphinidin.
- Studies on bark extract have shown antiviral, antibacterial, antiprotozoal, anticancer, hypoglycemic and diuretic properties.
- Study of dichlormethane extract of air-dried leaves
isolated β-sitosterol (1) and stigmasterol (2) in about 5:1 ratio, squalene (3) and lutein (4). (14)
- Study of methanolic extract of C. trifolia shoots yielded good amounts of phenolics, flavonoids, tannins, and alkaloids. HPLC analysis identified 8 phenolic and flavonoid compounds viz. gallic acid, catechin hydrate, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, sinapic acid, coumarin and kaempferol. (see study below) (20)
Properties
-
In India, plant is considered astringent, antibacterial, antiscorbutic, antitumor, hypoglycemic, and rubefacient.
- Plant used as diuretic,
- Root considered astringent.
- Studies have suggest antioxidant, antitumor, antiimplantation, antidiabetic, anticancer,
antibacterial, antinociceptive, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, mosquito larvicidal properties.
Parts used
Root, tubers, seeds, leaves.
 Uses Uses
Edibility
- Young leaves eaten as vegetable.
Folkloric
- Leaves in decoction considered antiscorbutic.
- Sap of the leaves also antiscorbutic.
- Root, ground with black pepper, is applied to boils.
- Root also used as astringent medicine.
- In India, roots are grounded with black pepper and applied as poultice on boils. Also used as a tonic stimulant in debility. Plant used for eye diseases (conjunctivitis, cataracts and night blindness).
- Infusion of seeds with extract of tubers used for diabetes.
- Paste of tubers applied to snake bites.
- Whole plant used as diuretic; also for tumors, neuralgia and splenic afflictions.
- Plant used as poultice for nose ulcers or a rubefacient.
Decoction used for fever. Juice used to treat itching on the scalp.
Others
- Veterinary: In India, climbers are wrapped around the neck of frantic bullock. Poultice of leaves used for yoke sores of bullock.
Studies
• Antioxidant: Study of two weeds, Chenopodium album and Vitis trifolia, showed significant reducing power and free radical scavenging effect on DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide radicals.  (1) Of various plant extracts of Cayratia trifolia evaluated for antioxidant activity using DPPH assay, a methanolic extract showed good antioxidant potential with IC50 of 43.396 ± 0.52 in vitro, 47.88 ± 0.04. (16)
• Anti-Tumor / Epifriedelanol: Study isolated epifriedelanol from V. trifolia, which exhibited antitumor activity in a potato disc bioassay. (2)
• Anti-Implantation Activity / Leaves: Study evaluated the antiimplantation properties of a petroleum ether extract of leaves in rats. Results showed potent dose-dependent antiimplantation activity. The exact mechanism of activity was not pinpointed by the study. (7)
• Anti-Diabetic Activity / Leaves: Study evaluated the hypoglycemic activity of C. trifolia using glucose uptake by isolated rat hemidiaphragm in vitro model. The extract showed a direct peripheral action on glucose uptake and suggests a potential for the treatment of diabetes mellitus caused by resistance to the stimulatory effect of insulin on GLUT-4 protein. (8)
• Anti-Diabetic Activity / Roots: Study evaluated the antidiabetic activity of roots in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Phytochemical studies yielded steroids, flavonoids, and alkaloids. Results showed C. trifolia ethyl acetate extract of roots possessed potent antidiabetic activity. (9)
• Novel PPARγ agonist / Possible Anticancer Option: Perixome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma (PPARγ) is a nuclear receptor family transcription factor expressed in several types of cancer. GC-MS analysis yielded 20 bioactive compounds of which cyclopentadecane, 9-Borabicyclo [3.3.1]nonane, 9-(2-propen-1-yloxy)-.1, 4,8,12,16-Tetramethylheptadecan-4- olide, Oxirane and Vitamin E showed the better glide score. The bioactive compounds may act as good agonist for PPARγ; and in the future, a potential anticancer therapeutic option. (10)
• Antibacterial / Alternative Treatment for Boils: An alcoholic leaves extract of Cayratia trifolia showed antibacterial property to boils caused by Staphylococcus aureus. (11)
• Larvicidal Against Culex quinquefasciatus: Study evaluated young and mature leaves of C. trifolia for larvicidal activity against 3rd instars larvae of Culex quinquefasciatus. The water extract of leaves yielded steroids, triterpene glycosides, essential oil, phenolics and diterpenes as secondary phytochemicals. Results showed C. trifolia leaf to have promise as a cost effective and potent larvicidal agent against C. quinquefasciatus. (12)
• CXCR4 Inhibitory Activity / Against Culex quinquefasciatus: CXCR4 (Chemokine Receptor type 4) is a drug target involved in many disease states including 23 types of cancer and several immunodeficiency disorders. Study evaluated the inhibitory activity of linoleic acid isolated from an ethanolic extract of C. trifolia against CXCR4. Results suggest the isolated compound linoleic acid may act as a novel inhibitor against CSCR4, with potential as a therapeutic agent for various types of cancers. (15)
• Antidiabetic / Antioxidant / Roots: Study evaluated the antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of C. trifolia root extract against STZ-induced diabetes in experimental rats. An ethanolic extract of root (500 mg/kg) showed significant (p<0.01) reduction in blood glucose (312-178 mg/dL), increase in body weight and serum insulin (1.28-2.26 IU/dL). GC-MS analysis showed relatively high concentration of ß-sitosterol. Oxidative stress induced decline in glutathione and catalase in liver and kidney tissues showed recovery to nearly normal. (17)
• Antinociceptive / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated a crude methanolic extract of aerial parts of Vitis trifolia for possible antinociceptive activit using acetic acid induced writhing model in mice. Results showed significant (p<0.001) reduction of number of acetic acid-induced abdominal (writhing) in mice at 250 and 500 mg/kg body weight, comparable to standard drug, diclofenac sodium. (19)
• Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory / Antidiabetic / Shoots: Study of optimized phenolic extract of C. trifolia shoots (PECTS) showed remarkable potential as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic agent. Out of 19 phytocompounds identified by GC-MS analysis, one compound, ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, acetate (3ß,22E) exhibited best binding with target proteins invovled in anti-inflammatory (Tnf-α and COX-2), antioxidant (SOD), and antidiabetic (α-amylase and reductase) activities. Non-toxicity was evident during in vitro cell toxicity assay against Vero cell line and in vivo acute toxicity study on BALB/c mice. (see constituents above) (20)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Gen info
Gen info
 Uses
Uses