
Family • Araliaceae
Lima-lima
Heptapleurum ellipticum (Blume) Seem.
FIVE FINGERS
Qi ye lian

| Scientific names | Common names |
| Heptapleurum ellipticum (Blume) Seem. | Arasagat (Ilk.) |
| Paratropia elliptica (Blume) Miq. | Galamai-amo (Tag.) |
| Schefflera elliptica (Blume) Harms | Kalakang (Bag.) |
| Sciodaphyllum ellipticum Blume | Karangkang (Bik.) |
| Accepted infraspecifics (2) | Kayangkang (Bik.) |
| Heptapleurum ellipticum var. ellipticum | Kokotimbazlun (Yak.) |
| Actinophylllum belangeri (Marchal) R.C.Schneid. | Lima-lima (Tag.) |
| Aralia moorei F.Muell. | Palan (Sul.) |
| Hedera terebinthinacea Wall. | Panagang (Tagb.) |
| Hedera venosa Wall. | Tagima (Bis.) |
| Hedera verticillata Span. | Tagilima (Bis.) |
| Heptapleurum micranthum (Miq.) Seem. | Tarangkang (S. L. Bis.) |
| Heptapleurum natale Ridl. | Tughik (Iv.) |
| Heptapleurum verticillatum (Span.) Seem. | Tuglima (Bis.) |
| Paratropia assamica K.Koch | Climbing umbrella tree (Engl.) |
| Paratropia crassa Blanco | Elliptic-leaved schefflera (Engl.) |
| Paratropia elliptica var. micrantha (Miq.) Miq. | Five fingers (Engl.) |
| Paratropia elliptica var. ovata Miq. | Schefflera vine (Engl.) |
| Paratropia elliptica var. riparia Miq. | |
| Paratropia elliptica var. tetraphylla Miq. | |
| Paratropia elliptica var. verticillata (Span.) Miq. | |
| Paratropia macrantha Miq. | |
| Paratropia micrantha Miq. | |
| Paratropia pubigera Brongn. ex Planch. | |
| Paratropia verticillata (Span.) K.Koch | |
| Polyscias odorata Blanco | |
| Schefflera agusanensis Elmer | |
| Schefflera belangeri (Marchal) Harms | |
| Schefflera elliptica var. microphylla F.M.Mull. | |
| Schefflera fukienensis Merr. | |
| Schefflera micrantha (Miq.) Ridl. | |
| Schefflera minimiflora Ridl. | |
| Schefflera nitida Merr. | |
| Schefflera odorata (Blanco) Merr. & Rolfe | |
| Schefflera pubigera (Brongn. ex Planch.) Frodin | |
| Schefflera stelzneriana Guillaumin | |
| Sciodaphyllum assamicum K.Koch | |
| Sciodaphyllum belangeri Marchal | |
| Sciodaphyllum verticillatum (Span.) Walp. | |
| Unjala rheedei Reinw. ex Blume | |
| H. ellipticum var. obliquinervium (Gamble) Lowry & G.M.Plunkett | |
| Schefflera elliptica var. obliquinervia (Gamble) Karthik. & Moorthy | |
| Schefflera venulosa var. obliquinervia Gamble | |
| Galamai is a local name for three different species of genus Schefflera, distinguished from each other by the leaf numbers and features: (1) Schefflera elliptifoliola Merr. (Galamai) (2) Schefflera insularum Seem. (Galamai-amo, kalangkang, kulolo, pararan) (3)Schefflera odorata Merr. (Galamai-amo, kalakang, lima-lima) | |
| Heptapleurum ellipticum (Blume) Seem. is an accepted species. KEW: Plants of the World Online | |
| Other vernacular names |
| CHINESE: Qi ye lian, Mi mai e zhnag chai (S. ellipitica). |
| MALAY: Ara bebari, Bunga kuku langsuir, Cenama gajah. |
| LAOTIAN: Lep meu nang. |
| OTHERS: Cenama, Gajah, Rawanito, Waghchavad. |
|
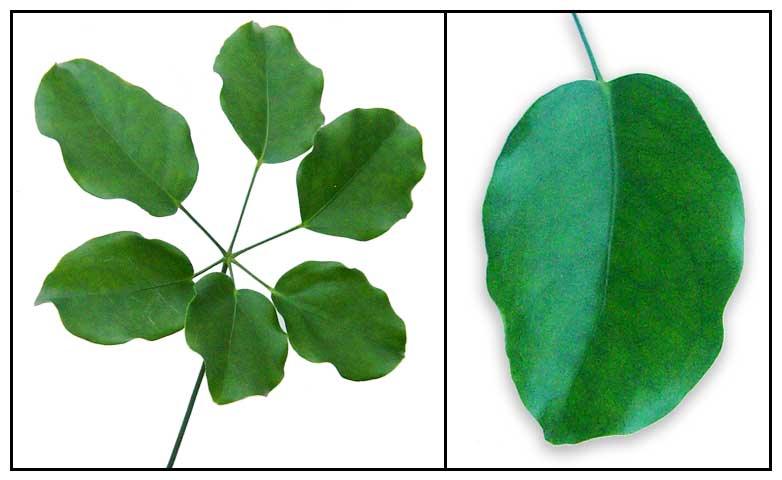
Gen info Botany • Growth form: A woody climber or straggling shrub, up to 10 m tall. Foliage: Alternate, stalked, palmate leaves have 4-7 leaflets that are 6-18 by 2.5-10 cm. Flower: Greenish flowers are arranged in a 10-flowered cluster. Fruits: Fruits are round to egg-shaped, ripening from yellow or orange to black. (20)
Parts utilized Studies Availability |
 |
PHOTOS / ILLUSTRATIONS |
| Photos © Godofredo Stuart / StuartXchange |
| OTHER IMAGE SOURCE: Heptapleurum ellipticum fruits / Bruce Gray / CC BY-SA 4.0 International / Cliick on image or link to go to source page / Wikimedia Commons |
Additional
Sources and Suggested Readings |
• |
DOI: It is not uncommon for links on studies/sources to change. Copying and pasting the information on the search window or using the DOI (if available) will often redirect to the new link page. (Citing and Using a (DOI) Digital Object Identifier) |
| List of Understudied Philippine Medicinal Plants |
| New plant names needed The compilation now numbers over 1,500 medicinal plants. While I believe there are hundreds more that can be added to the collection, they are becoming more difficult to find. If you have a plant to suggest for inclusion, native or introduced, please email the info: scientific name (most helpful), local plant name (if known), any known folkloric medicinal use, and, if possible, a photo. Your help will be greatly appreciated. |
• |
 |