  Gen info Gen info
- Onagraceae are a family of flowering plants known as the willowherb family or evening primrose family, with about 650 species of herbs, shrubs, and trees in 17 genera. The family is widespread, occrring on every continent from boreal to tropical regions. The family is characterized by flowers with usually four sepals ad petals. (15)
- Ludwigia is a genus of about 82 species of aquatic paltns with a cosmpolitan but mainly tropical distribution. (17)
- Ludwigia hyssopifolia is a species of flowering plant in the genus Ludwigia, native to the New World Tropics and widely distributed to the rest of the world's tropics. (16)
- A serious weed of rice paddies. The common name "seed box" likely alludes to its efficiency in seed production: a single plant can produce 250,000 seeds. (16)
- Etymology: The family Onagraceae was named after the genus Onagra (now known as Oenothera) in 1836 by John Lindley in the second edition of A Natural System of Botany. (15) The genus Ludwigia was named by Carl Linnaeus after Christian Gottlieb Ludwig (1709-1773).
(17) The specific epithet hysspifolia derives from Greek words, meaning "hyssop leaf", referring to the leaf shape and size that resemble the leaves of the aromatic herb hyssop.
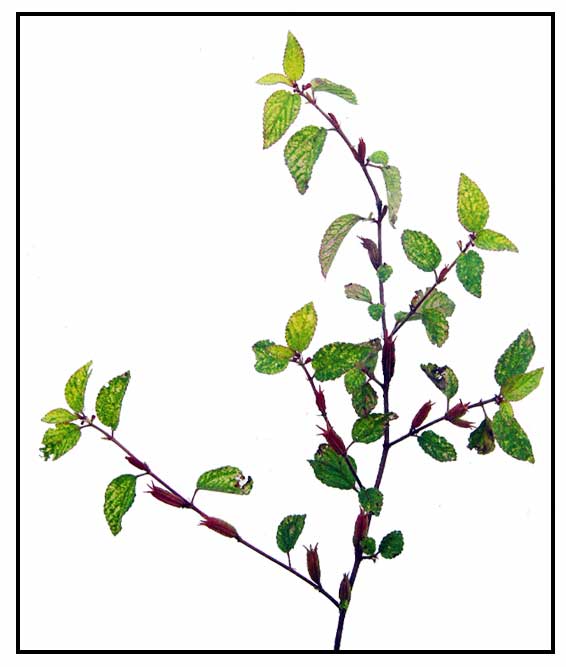
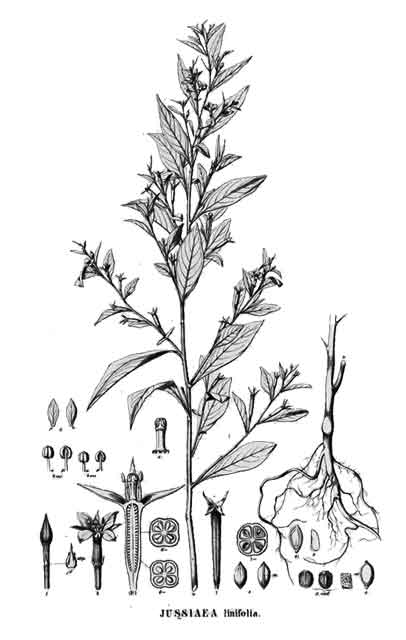 Botany Botany
• Pasau-na-hapai is an erect, branched, smooth annual, 20 to 60 centimeters high, with
green or purplish, 3- or 4-angled or winged stems, and spreading
3-angled branches. Leaves are narrowly elliptic-lanceolate or oblong lanceolate,
4 to 10 centimeters long. Flowers occur singly and without stalk in the axils of leaves. Calyx-tube is slender and about 8 millimeters long, with 4 green,
lanceolate, nearly 4 millimeter long calyx-lobes. Petals are 4, yellow, narrowly
oblong-elliptic, and as long as the sepals. Stamens are 8, ovary
4-celled, ovules many in several axil rows in each cell. Fruits are capsules, green or purplish, about 3 centimeters long,
and 1 to 2 millimeters in diameter. Seeds sometimes faintly visible through
the walls.
• Growth form: Usually an herbaceous annual with erect growth form, but occasionally a perennial with a stem that is woody near the base. Foliage: Leaves are elliptic to lanceolate with entire leaf margin (10 cm long, 1-3 cm wide). Flowers: Yellow flower is composed of 4 obovate petals (0.2 - 0.4 cm long) arranged in a cross-like pattern. Yellow petals later turn orange-yellow. Fruit: Dry, dehiscent fruits are known as capsules. Fruits produce two types of seed. Seeds from the bottom of the capsule are darker and longer (0.9 cm long) than those on top (0.5 cm long). (Flora & Fauna Web)
 Distribution Distribution
- Introduced. (6)
- Cryptogenic. Circumtropical. Sometimes considered native. Invasive outside its native distribution range. In pools, along rice paddies, canals and shallow ditches, river edges, waterlogged wastelands, etc. Lowlands.
(14)
-
Throughout the
Philippines, in open, damp places, old rice paddies, margins
of streams, etc. at low and medium altitudes.
- Considered an extremely widespread weed of rice and wetlands across three continents. (8)
- Probably of American origin.
- Native to Bolivia, Brazil North, Brazil Northeast, Brazil South, Brazil Southeast, Brazil West-Central, Central American Pacific Is., Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Leeward Is., Mexico Gulf, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, Nicaragua, Northern Territory, Peru, Queensland, Suriname, Trinidad-Tobago, Venezuela, Venezuelan Antilles, Windward Is. (6)
- Now pantropic.
Parts
utilized
Whole plant, leaves, roots.
Constituents
- Phytochemical studies yielded vitexin, isovitexin, orientin and isoorientin.
- Ethanol extract yielded one new compound, 6β, 24 hydroxy tormnetic acid [2α, 3β, 19α, 6β, 24- penta hydroxylurs-12-en-18-oic acid (1) together with seven known compounds, viz. xanthyletin (2), (+) trans-decursidinol (3), β-sitosterol (4), β-sitosterol-β-D- glucopyranoside (5), 6β, 23-hydroxy tormentic acid (6), 23-hydroxy tormentic acid (7) and 6β, 23-hydroxy tormentic acid (8). (9)
-
Study of purified petroleum ether and ethyl acetate fractions from L. hyssopifolia yielded 9 natural products, namely: ethyl gallate (1), vanillin (2), trans-p-hydroxycinnamic acid (3), trans-p-hydroxy-ethyl cinnamate (4), ozoroalide (5), scopoletin (6), de-O-methyllasiodiplodin (7), syringaldehyde (8), and 3,3′-dimethoxy-4,4′-dihydroxy-stilbene (9). (see study below) (22)
- Study isolated a pair of new isocoumarin derivative enantiomers, (S)-(-)-3-(3,3-dichloro-2-hydroxy-propyl)-4-chlorine-6,8-dihydroxy-isochromen-1- one (1a) and (R)-(+)-3-(3,3-dichloro-2-hydroxy-propyl)-4-chlorine-6,8-dihydroxy-isochromen-1- one (1 b), as well as seven known compounds (2–8). (see study below) (23)
- Phytochemical analysis of methanol extract of aerial parts isolated four known compounds: ß-sitosterol (1), oleanolic acid (2), 3-O-ß-D-glucopyranosyl-ß-sitosterol (3), and ellagic acid (4).
(see study below) (25)
Properties
- Considered astringent, anthelmintic, carminative and diuretic.
- Studies have suggested analgesic, anti-inflammatory, cytotoxicity, antidiarrheal, antibacterial, anthelmintic, antitumor, antioxidant, antiproliferative, apoptosis-inducing properties.
 Uses Uses
Edibility
- In Indo-China, young parts are used in soup. In Malaysia, cooked and eaten as vegetable. (18)
Folkloric
- Used for cold-fever, swelling pain in the throat, inflammation of the
mouth cavity.
- Used for enteritis-diarrhea, eczema, and furuncle.
- The decoction
of dried materials used as gargle for mouth ulcer.
-
Pounded fresh material may be
applied as poultice to area afflicted by eczema.
- In Bangladesh and India, decoction used for diarrhea and dysentery, flatulence, leucorrhea and hemoptysis. Leaves used for poulticing in orchitis and neck gland enlargement. Decoction used as vermifuge and purgative. (•) In Bangladesh, fresh leaf juice given for treatment of hysteria. Juice also used for treatment of tetanus. (24)
- Infusion of root is swallowed by the Malays for syphilis.
- In Celebes, infusion of roots used for poulticing pimples.
- In Nigeria, decoction of leaves use for treatment of malaria. (13)
Others
- Dye: In the Philippines, plant used in making a black dye.
Studies
• Piperine / Anti-tumor / Antibacterial: Study isolated an alkaloidal constituent, piperine, which showed antitumor and antibacterial activity. Its inhibitory effect on crown-gall tumor suggests potential for exploitation of the plant species for cancer prevention and treatment. On antibacterial study, it showed good activity against Shigella dysenteriae, S aureus and B subtilis. (1)
• Antidiarrheal: Study of methanol extract of Ludwigia hyssopifolia showed significant antidiarrheal property by reducing diarrheal episodes in castor oil and serotonin induced diarrhea in laboratory mice. The extract reduced gastrointestinal motility by 53.8% at dose of 100 mg/kbw. Standard drug was loperamide. (2)
• Analgesic: Study evaluated the analgesic activity of a methanolic extract of Jussiaea hyssopifolia plant in Swiss albino mice using a hot plate method. Results showed significant analgesic effect compared to standard drug diclofenac. (4)
• Anhelmintic: Study evaluated the methanolic extract of the entire plant of Jussiaea hyssopifolia for anthelmintic activity against earthworm Pheretima posthuma. Results showed significant anthelmintic effect in comparison to standard drug. (5)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Analgesic / Diuretic / Whole Plant: Study evaluated hexane, ethylacetate, and methanol extracts of whole plant parts of Ludwigia hyssopifolia for anti-inflammatory, analgesic, diuretic activities. Hexane and EA showed maximal inhibition of carrageenan-induced paw edema. All extracts showed significant inhibition of writhing reflex. All extracts exhibited good diuretic action. (7)
• Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory / Bark: Study evaluated the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ethanolic bark extract on experimental animal models. Results showed central and peripheral analgesic activity, as well as anti-inflammatory effect, which may be due to various chemical constituents, specially flavonoids, tannins, alkaloids, or terpenoids. (10)
• Hepatoprotective / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the methanolic extract of aerial parts for in vitro method by measures of ALT, AST, and LDH and in vivo methods by measures of serum biochemical parameters and histological liver changes. The LHME exhibited significant (p<0.01) hepatoprotective activity in both in vivo and in vitro models, which may be attributed to its antioxidant property. (11)
• Anti-Inflammatory / LD50 / Leaves: Study evaluated various extracts of leaves for phytochemical profile, acute toxicity, and anti-inflammatory properties. Phytochemical analysis of leaf extract yielded alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, cardiac glycosides, saponins (steroids / triterpenes) and carbohydrates. The median lethal dose (LD50) of extracts by oral route was greater than 5000 mg/kg. Results showed significant decrease (p<0.05) of carrageenan induced paw edema in rats, with the hexane extract showing highest activity compared to other extracts. (12)
• Antiproliferative on Human Hepatic Cancer (HepG2) Cells / Antioxidant / Leaves and Whole Plant: Study of whole plant methanol extract of L. hyssopifolia
and leaf extract of L. adscendens showed greatest antioxidant properties in DPPH radical scavenging assay with IC60s of 44.48 and 26.11 µg/mL, respectively. The ME of L. hyssopifolia leaves showed most potential anti-HepG2 activity. (19)
• Antibacterial / Whole Plant: Study evaluated the most effective fractionated extracts of Ludwigia hyssopifolia for antibacterial activity against pathogens, including B. cereus, S. aureus, E. coli, S. typhi, and Helicobacter pylori through agar diffusion technique and microtiter broth dilution method. Largest yield was from the aqueous extract. The ethyl acetate extract showed abundance in phenolics and flavonoid compounds. Fractionation enhanced the antibacteria effect of the extract. Extracts showed broad spectrum activity against all tested bacteria, particularly H. pylori. (20)
• Induction of Apoptosis in Throat Cancer Cell / Ursolic Acid: Previous studies have reported anti-laryngeal cancer benefits of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether fractions of ethanolic extracts. Study assessed the anti-throat cancer effects of two derivatives of ursolic acid extracted from L. hyssopifolia (LH-CUAD) using throat cancer cell lines Hep-2 and FaDu and Hep-2 tumor-bearing nude mice. LH-CUAD significantly inhibited proliferation and migration of throat cancer cells without prominent toxicity. LH-CUAD induces apoptosis in both invivo and invitro models of throat cancer via activation of the mitochondrial pathway, inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway and initiating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Study suggests LH-CUAD
has potential for a novel approach to clinical management of throat cancer. (21)
• Cytotoxicity Against Human Laryngeal Cancer Hep-2 Cell Line: Study of purified petroleum ether and ethyl acetate fractions from L. hyssopifolia yielded 9 natural products, namely: ethyl gallate (1), vanillin (2), trans-p-hydroxycinnamic acid (3), trans-p-hydroxy-ethyl cinnamate (4), ozoroalide (5), scopoletin (6), de-O-methyllasiodiplodin (7), syringaldehyde (8), and 3,3′-dimethoxy-4,4′-dihydroxy-stilbene (9). Four compounds exhibited cytotoxic effects on human laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cell line. Compounds 5 and 7 were effective against TU212 cell line and significantly inhibited cancer cell growth in a dose- and time-dependent manner. (22)
• Isocoumarin Enantiomers / Anticancer / Increase Glucose Uptake: Study isolated a pair of new isocoumarin derivative enantiomers, along with seven known compounds. In invitro assays. compounds 5 and 8 can inhibit human laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cell line growth in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Compounds 2 and 4 showed effects on increasing glucose uptake in vitro. Compound 2 showed strong glucose uptake in L6 cels, with 1.8-fold enhancement. (see constituents above) (23)
• Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activityy / Aerial Parts: Helicobacter pylori is considered a main cause of peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma. Study evaluated five extracts and fractions of aerial parts of Ludwigia hyssopifolia for anti-H. pylori activity by disc diffusion method. All five extracts and fractions exhibited moderate activity, with methanol extract showing strongest inhibitory activity with inhibition zome of 17mm. Phytochemical analysis of methanol extract isolated four known compounds: ß-sitosterol (1), oleanolic acid (2), 3-O-ß-D-glucopyranosyl-ß-sitosterol (3), and ellagic acid (4). Ellagic acid and oleanolic acid were considered major effective constituents for anti-H- pylori activity. (25)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
Seeds in the cybermarket. |

![]()

