|
 Gen info Gen info
- Equisetum (horsetail) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of vascular plants that reproduce by spores rather than seeds. (14)
- Equisetum is a "living fossil," the only living genus of the entire subclass Equisetidae, which for over 100 million years was much more diverse and dominated the understorey of late Paleozoic forests. Modern horsetails first appeared during the Jurassic period. (14)
- Etymology: "Horsetail" is often used for the entire group, which refers to the branched species resembling a horse's tail. The genus name Equisetum means "horse hair" derived from Latin equus (horse) and seta (bristle). (14) The specific epithet ramosissimum means "much branched", referring to the numerous whorls of branches at each node.
Botany
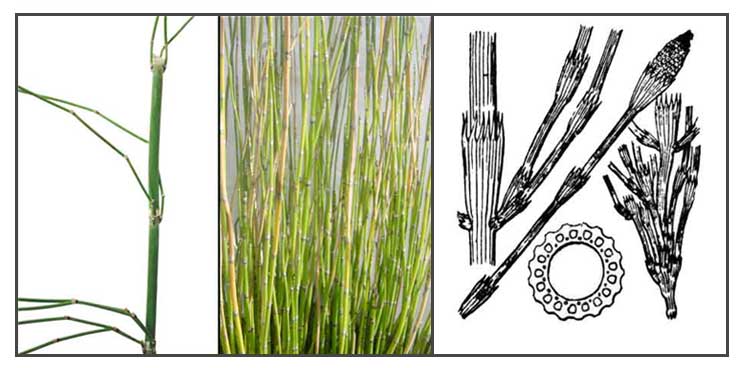
• Putod is a perennial herb, with jointed
and branched rootstock. Roots are in whorls from the nodes.
Stem is hollow and noding, the length of the internode 2 to 6 centimeters with
longitudinal striations at the surface. Leaves are obsolete,
reduced to scales around the node. Cones (strobili) are oblong, green-yellow in color depending
on maturity, terminal or spirally borne on the tip of the stem.
• The species differs from Equisetum debile in that the fertile stems are much branched, and are grooved and rough.
• Horsetail with untidy branches from the lower parts (which may be prominent or not apparent), with or without main upright stems, able to form a colony from underground roots. Rocky ground tends to constrict root-spread and favors a bushy appearance, unrocky ground favors more slender plants arising from spreading roots, and trampling or cutting affects shape. The general color may have a blue-grey tinge, sometimes quite strongly, the stem when broad is fairly hollow and compressible, narrower branches rather tough and wiry, the stem ridges are conspicuous (not fine and obscure) and slightly rough. The fertile cones when visible are from stems arising as part of the main plant (not arising early separately) and have pointed cone tips (sometimes obscure).
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines. (5)
-
Widely distributed
throughout the Philippines at medium to high altitudes (about
1,000 to 6,000 ft above sea level).
-
Usually found along exposed
stream embankments on sandy to stony soil.
-
Easily overlooked
because it blends with grassy landscape. Easily grown in ordinary
garden soil.
- Also native to Albania, Algeria, Altay, Angola, Assam, Austria, Azores, Baleares, Bangladesh, Belarus, Belgium, Borneo, Botswana, Bulgaria, Burundi, Cambodia, Canary Is., Cape Provinces, Cape Verde, Central European Russia, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Corse, Cyprus, Czechia-Slovakia, DR Congo, East European Russia, East Himalaya, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Fiji, France, Free State, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Gulf States, Hainan, Hungary, India, Inner Mongolia, Iran, Iraq, Italy, Japan, Jawa, Kenya, Korea, Kriti, Krym, Kuwait, KwaZulu-Natal, Laos, Lebanon-Syria, Lesotho, Lesser Sunda Is., Libya, Madagascar, Madeira, Malawi, Malaya, Maluku, Manchuria, Mauritania, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar, Namibia, Nansei-shoto, Nepal, Netherlands, New Caledonia, New Guinea, North Caucasus, Northern Provinces, Northwest European Russia, NW. Balkan Pen., Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Poland, Portugal, Qinghai, Romania, Réunion, Sardegna, Saudi Arabia, Sicilia, Sinai, Solomon Is., Somalia, South European Russia, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan-South Sudan, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Taiwan, Tanzania, Thailand, Tibet, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Türkey, Türkey-in-Europe, Uganda, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vanuatu, Vietnam, West Himalaya, West Siberia, Western Sahara, Xinjiang, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe. (5)
Components
- GC-MS analysis of aerial parts for chemical composition of essential oil yielded 37 compounds, composed mainly of terpenoids with monoterpenoids comprising 41.7% and sesquiterpenoids 36.4%. α-Bisabool oxide A (12.3%) and cuminaldeyde (9.8%) were identified as major constituents. (see study below) (8)
- Phytochemical screening for secondary metabolites yielded alkaloids, unsaturated steroid, deoxysugars, flavonoids, tannins and polyphenols. (12)
- The chemical quantification revealed appreciable levels of phenolic compounds. The results of HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS highlighted the presence of kaempferol3-O-sophoroside7-Oglucoside, kaempferol3,7-O-diglucoside, vanillin, ferulic acid and tannic acid. (see study below) (20)
 Properties
Properties
- Sweet and slightly bitter tasting.
- Cleanses the liver and clears the eyesight.
- Diuretic and astringent.
- Edibility concerns: If eaten over a long period of time, some species of horsetail can be poisonous to grazing animals, including horses. The toxicity is attributed to thiaminase, which can cause thiamin (B1) deficiency. (14)
- Studies have shown antioxidant, diuretic, CNS depressant, anti-melanogenesis, nephroprotective, antidiabetic, antiobesity, weight reducing, antimicrobial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anticariogenic, antihyperlipidemic properties.
Parts
utilized
- Stem.
- Collected year round.
- Rinse, cut into pieces, and dry under the sun.
Uses
Edibility
• Horsetails are regularly consumed. The fertile stems bearing strobili of some species can be cooked and eaten like asparagus. Young plants are eaten cooked or raw, but caution is advised. (see above)Â (14)
Folkloric
• In the Benguet Province, locals used a decoction of fresh leaves to treat difficulty in urination and other kidney troubles. Decoction of leaves and roots used to treat "pasma." (12)
•
Used for hypertension, reddening and
swelling pain in the eye, pterygium of the cornea.
• Used for diarrhea, jaunditic hepatitis, and renal lithiasis.
• Dosage: 15 to 30 gms of dried material in decoction.
• In China, decoction of whole plant used from wounds and ulcers. Also, used as antitussive and diuretic.
• In India, tribals of Melghat region, the entire plant as cooling medicine for gonorrhea. (13)
• In India, plant paste applied to bone fracture; young cones used to treat kidney problems. (10)
• Used to improve fertility in women. In Africa, rhizome decoction used to facilitate fertilization in barren women.
• In Turkey, decoction used as diuretic
and for removing kidney stones. (9)
• In Malaysia and Indonesia, stems are powdered and made into ointment for external application on bruises, fractures, and arthritis.
• In Moroccan traditional medicine, used as diuretic and for treatment of diabetes.
Others
• Fodder toxicity: Eaten over a long period of time, some species of horsetail can be poisonous to grazing animals, especially horses. (14) Poisonous when consumed in large quantities probably due to large quantities of the toxic principle, the enzyme thiaminase, which destroys vitamin B1, Livestock may appear drunk and may harm themselves. (24)
• Cleaning / Scouring: Leaves used for cleabubg cooking and eating utensils. Sandpaper quality of leaves allow for use in shapping and smoothing tools, ornaments, and weapons.
Studies
• Antioxidant:
Study on scavenger activities of three equisetum species, including E
ramosissimum, showed E telmatela to have the most scavenger and antioxidant
activity. (1)
• Diuretic / Toxicity / CNS Depressive Activity:
An ethanol extract administered to Swiss albino mice showed moderate level of toxicity and central nervous depressive properties. The ethanol extract also exhibited an interesting diuretic activity in male Sprague-Dawley rats when administered orally and intraperitoneally. (4)
• Protective Against Oxidation, Melanoma, and Melanogenesis: Study compared five extracts for inhibiting effects on three human malignant melanomas: A375.A375.S2 and A2058. The EA fraction discontinued or terminated free radical chain reactions. In human melanoma, EA and DM extracts affected the viabilities of melanoma cells and showed low toxicity in both normal human cells, HaCaT cells and fibroblasts. The EA extract inhibited cellular melanin production. Overall, biofunctional activities of EA extract in food and cosmetics protect against oxidation, melanoma and melanin production. (6)
• Biochemical and Hematological Effects in Pregnancy: Study investigated the maternal toxicity of aerial parts of Equisetum ramosissimum on pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats. Daily gavage doses of ER extract produced significant differences in biochemical and hematological parameters in pregnant rats. Â (7)
• Essential Oil / Carvacrol / Aerial Parts: Study of aerial parts for chemical composition of essential oil yielded 37 compounds. α-Bisabool oxide A (12.3%) and cuminaldeyde (9.8%) were identified as major constituents. The high content of monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids as well as the presence of carvacrol was unusual as compared to other Equisetum spp. Carvacrol has reported ovicidal effect on neonate larvae, and suggests further study on the question of toxicological effect of essential oil on reproductive health in animals. (8)
• Flavonoids / Hepatitis Treatment / Invention: Invention relates to Chinese materia medica preparation with total flavonoids of E. ramosissimum Desf. for the treatment of hepatic diseases, for example, viral hepatitis with jaundice. The preparation consists of total flavonoids of E. ramosissimum 0.3-85% of the extract as active ingredient and 15-99.7% of pharmaceutical adjuvants, in various preparations (injection, oral solid or liquid form, cream) where the active ingredient of E. ramosissimum is not less than 50%. Invention is believed to have antiviral efficacy in acute and chronic hepatitis, safe and free from toxicity, curative and convenient. (11)
• Antioxidant / Potential for Urinary Tract Infction: Study evaluated stem extracts of plant for treatment of UTIs against selected pathogenic bacteria. GC-M analysis yielded 24 phytoconstituents with major compounds of linoleic acid, palmitic acid, nonacosne, hexahydrofarnesyl acetone, and octacosane. The ME yield maximum TPC and TFC with 600.02 mg GAE/g and 631.38 mg QE/g respectively. MIC were 31.25 of aqueous and methanol extracts against R. equi and V. cholerare. Methanolic and petroleum ether extract inhibited B. subtilis with MIC of 31.25 µg/mL. (16)
• Nephroprotective effect on STZ-Dabetic Rats / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the effect of aerial part of E. ramosissimum to control diabetic nephropathy on STZ-induced diabetic rats. Methanol and ethanol extracts revealed TPC of GAE of 7.62 and 8.97 mg/g, respectively, and flavonoids of QE 8.87 amd 12.86 mg/g, respectively. Both ME and EE contained isoferulic acid, iso-orientin, myristic acid, linoelaidic acid, rutin, and 3-glu-7-Rha quercetin. The EE significantly impaced STZ-induced diabetic mice by reducing fasting glucose levels, creatiine, and urea (p<0.005).Study suggests potential for effects on diabetes-related complications. (17)
• Effect on Body Weight effect on STZ-Diabetic Rats / Aerial Parts: Stud evaluated the effect of E. ramosissimum on levels of leptin, ghrelin, and their ratio in association withe body weight changes in animals receiving standard and high fat diet. Significant reduction in serum leptin/ghrelin ration was positively correlated with body weight and serum leptin levels. Er extract possessed promising characteristics on being introduced as dietary supplements and weight control regiments. It restored weight of obese animals who gained weight on a high-fat diet. Studies are suggested to reveal the translational potentials of Er extract and its vital effects on adipokines. (18)
• Antioxidant / Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated the potential use of crude butanolic (BE) and methanoli (ME) extracts pf E. ramosissimum in the management of pain inflammation, and oxidative stress, and their chemical characterization. The BE showed maximum IC50 on DPPH assay (0.064 mg/,L). Th BE also exhibited interesting antinociceptive effect with writhe inhibition of 3.83 at 600 mg/kg, increased the latency period on hot-plate test at 14.985 at 400 mg /kg at 120 min. There was also significant inhibited of rat-paw edema and ear edema for both extracts at dose of 400 mgkg. (see constituents above) (20)
• Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles / Anticariogenic / Antimicrobial Against S. mutans: Study reports on the synthesis of Cerium oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of E. ramosissimum as both reducing and stabilizing agent and to evaluate its activity against cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Antibacterial activity was evaluated using agar well diffusion method. Antibacterial assay showed significant inhibition zones of 20-32 mm against S. mutans. The green synthesized CeO2-NPs exhibited promising antimicrobial activity against S, mutans, suggesting potential for dental applications. (21)
• Antihyperlipidemic / Leaves: Study evaluated the anti-hyperlipidemic effect of ethanolic leaf extract of E. ramosissimum alone or in combination with Atorvastatin in rats. An in-vivo study on healthy standard diet-fed animals and an induced-hyperlipidemic model showed a significant (p<0.05) reducing effect alone or in combination with Atorvastatin. (22)
• Antioxidant / Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory: Study evaluated the potential use of crude butanolic (BE) and methanolic (ME) extracts of E. ramosissimum in the management of pain, inflammation, and oxidative stress. HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS studies highlighted the presence of kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside-7-O-glucoside, kaempferol3,7-O-diglucoside, vanillin, ferulic acid and tannin acid. BE exhibited antinociceptive effect with writhe inhibition of 3.83 at 600 mg/kg, increased latency period on hot plate test 14.98S at 400 mg/kg after 120 min. Both BE and ME contained significant amount of flavonoids, especially kaempferol derivatives, which may explain the effects. (23)
Availability
Wild-crafted. |



