 Gen info Gen info
- Solanum lasiocarpum is of interest to botanists because of its close resemblance and close relation to South American species, the cocona (S. sessiliflorum), the naranjilla (S. quitoense), and the pseudolulo (S. pseudolulo). Grown outside of their native range, these four plants will readily hybridize, producing sterile offspring, and, thus, the potential the enhance the commercial availability of each of the species elsewhere in the world. (4)
- Taxon notes: The binomial "Solanum indicum" is confusing to both lay people and academics due to the many authorities that have attempted to pin it down taxonomically. Consequently when one finds a photo or a text referring to "Solanum indicum" one is never sure if it refers to "Solanum anguivi" or "Solanum violaceum" or even "Solanum ferox". It has been rejected by taxonomists as the following notes from USDA - ARS - GRIN attest but the literature is riddled with "Solanum indicum" so all the common names associated with it become even more unreliable than usual.
- "Solanum indicum L., nom. rej., a rejected name (nomen utique rejiciendum) under Vienna ICBN Art. 56 & App. V that is unavailable for use.
- Hepper, F. N. 1978. (456,457) Proposals to list Solanum indicum L. and Solanum sodomeum L. as rejected names under Article 69 of the ICBN. Taxon 27:555." (Sorting EGGPLANT names / MULTILINGUAL MULTISCRIPT PLANT NAME DATABASE)
 Botany Botany
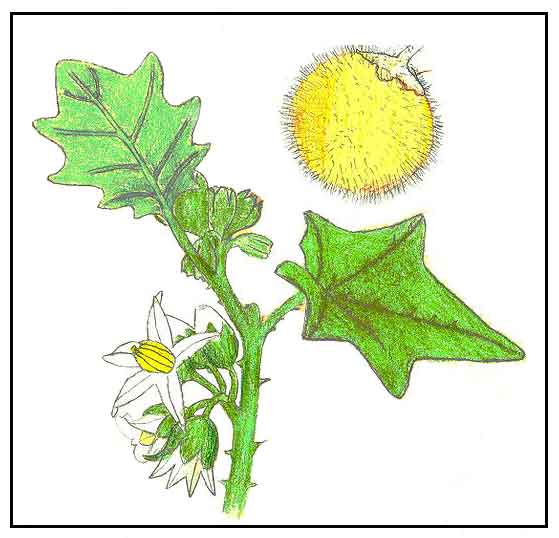
• Talong-pipit is an erect undershrub, 0.3 to 1.5 meters high. Stems are much branched, very prickly, and bearing compressed, stout, often recurved prickles. Leaves are ovate, 3.5 to 15 centimeters long, 2.5 to 8 centimeters wide, lobed or pinnatifid in the margins, blunt or pointed at the tip, pointed at the base, and stellately woolly beneath. Leaves in the branchlets are much smaller. Flowers are blue, borne in extra-axillary racemes. Calyx-lobes in flower are triangular, very woolly, unarmed, or furnished with slender, straight spines. Corolla is broadly triangular, 2 to 2.5 centimeters long, and hairy on the outside. Fruit is yellow, rounded, about 1.5 centimeters in diameter.
• Herbs or subshrubs, erect or spreading, 1-1.5 m tall, armed, densely pubescent throughout with pale yellow, many-celled stellate hairs. Stems and branches stout, with flat, erect or slightly recurved prickles 1-8 mm. Petiole 3-8 cm, often with stalked, stellate hairs and erect prickles; leaf blade ovate, 10-20 × 8-18 cm, pubescent as on stems, denser abaxially, prickly along veins on both surfaces, base truncate or subhastate, margin 5-11-sinuate lobed, apex acute. Inflorescences extra-axillary, several flowered, scorpioid-racemose, 1.2-2 cm; peduncle ca. 3 mm. Flowers andromonoecious. Pedicel ca. 1 cm. Calyx lobes ovate, 8-10 mm. Corolla white, subrotate, 1-1.2 × 2 cm. Filaments very short; anthers lanceolate, acuminate, 7-8 mm. Style ca. 9 mm, glabrous. Fruiting pedicel erect, 1-1.5 cm. Fruiting calyx somewhat enlarged, reflexed. Berry orange, globose, ca. 2 cm in diam., densely stellate hirsute, tomentum persistent. Seeds brown, ca. 2 mm in diam. (Flora of China)
 Distribution Distribution
- Native to the Philippines. (1) (2)
-
Throughout the Philippines. Generally at low to medium elevation, up to 2000 m; disturbed sites such as foerest clearings, second-growth thickets, roadsides, and wastelands. (20)
- Also native to Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Bismarck Archipelago, Borneo, Cambodia, China South-Central, China Southeast, India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Maluku, Myanmar, New Guinea, Queensland, Solomon Is., Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam. (1)
- Also reportedly grown in southernmost France and Italy.
Constituents
• Fruit contains solanin and solanidine.
•
Study of seeds isolated two new coumarins,  (E)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-5-methoxy-2H-[1,4]dioxino[2,3-h]chromene-3,9-dione (indicumin E, (1) and 7-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-3-(4′-hydroxy-3′-methoxyphenyl)-coumarin (2), together with two known coumarins isofraxidin (3) and fraxetin (4). (5)
• Study yielded isoangulvine, protodioscin, solasonine and solamargine, together with steroidal glycosides, named indiosides A-E, obtained from the fruits and roots. (11)
• Proximate nutrient composition of fruit per 100 g of edible portion yields 89.5% moisture, 1.1% protein, 0.9% fat, 5.8% carbohydrate, 1.75% crude fiber, and 0.8% ash. Mineral composition is 27 mg phosphate, 188 mg potassium, 3 mg calcium, 6 mg magnesium, 0.6 mg iron, 2 mg manganese, 0.6 mg copper, 5.2 mg zinc, and 8 mg vitamin C (Voon & Kueh, 1999; Shariah et al, 2013).
(15)
Properties
- Plant is considered cordial, aphrodisiac, astringent and resolvent.
- Root is considered diuretic, expectorant, diaphoretic and stimulant.
- Fruit is considered tonic and laxative.
- Studies have suggested
antioxidant, hepatoprotective, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, antitumor, cytotoxic, anticariogenic, laxative, anthelmintic properties.
Parts used
Roots, seeds, fruits, leaves.
 Uses Uses
Edibility
- In the Philippines, fruits used as ingredient in pinakbet and salad.
-
Fruits used in the preparation of curries, chutneys and preserves.
- In India, fruit used as sour-relish in curries.
- The unique sour taste, which increases as the fruit ripens, is prized as a vegetable ingredient, food flavoring, and as paste in chili sauce.
- Cooked with seafood or made into soup with pork or fish.
- Fruit is added in cooking, believed to reduced the fishy odor
of fish or the fattiness of pork.
- In Thailand, a special sauce, nam prek, is made from the fruit.
Folkloric
-
Used for asthma, febrile conditions, dry coughs, colic with flatulence, and worms.
- In the Philippines, used for treatment of syphilis.
- Decoction of leaves used for dysuria.
- Root used as diuretic; used in dropsy and as expectorant, for coughs and catarrhal affections.
- Vapor of burning seed used for odontalgia.
- In Malaya, root is pounded and the pulp pressed on ulcerated sores.
- In Java, decoction of leaves drunk as diuretic.
- Root, taken internally, used for difficult childbirth and toothaches; also, for fever, worms and colic, and skin diseases in children.
- Juice of the leaves with fresh juice of ginger is used for vomiting.
- Fruits and leaves, rubbed with sugar, applied externally for skin itches.
- Fruit used as tonic and laxative.
- In China, used as anti-inflammatory and wound healing herb.
- Leaves used as poultice for swellings. Decoction of roots drunk for violent body pains and post-prandial discomfort. Decoction used for treatment of syphilis. Root decoction used for bathing for fever. Root poultice used for itches, cuts, wounds, and bruises. Seed used for treating toothache; fumes from burned seeds inhaled. (3)
- In Laos, used for the treatment of cough.
- In Bangladesh and India, used for treatment of coughs, asthma, fever, vomiting, sore throat, gonorrhea, and female sexual disorders. (3) Used by traditional medical practitioners for treatment of syphilis and toothache. (14) Roots steeped in water drunk twice daily to treat chickenpox. Decoction of whole plant (seeds, blossoms, fruits, leaves, stem and roots) are boiled until reduced, and taken daily to treat typhoid. Poultice of crushed seeds applied to abscesses. For allergies, entire plant soaked with leaves of Azadirachta indica, rhizomes of Curcuma longa, roots of Flagellaria indica, bark of Alstonia scholaris, and leaves or bark of Justicia adhatoda, and the water drunk for two weeks. For fever, in Uttarakhand, India, seven leaves are placed on the head during sleep for three nights. Root decoction drunk for the same purpose. The Bodo tribes of Assam keep dried flowers or seeds in their mouth as a treatment of tooth decay. (15)
- The Kaviraj use S. lasiocarpum in combination with Piper nigrum, Cinnamomum tamala, C. verum, and Piper longum for treatment of influenza. In combination with Azadirachta indica, Justicia adhatoda, Trichosanthes dioca, used for treatment of leprosy. (13)
Studies
(Note) Studies include published studies on Solanum lasiocarpus and studies from previous pages of S. indicum and S. ferox (Tarambulo). The species have been subject of taxon conflicts, and attribution of scientific studies are likkewise fraught with conflicts. Also, in the process of merging the pages, the links for earlier studies on Solanum indicum are no longer available. Studies below are for both Solanum lasiocaepum and its synonym S. indicum. Studies will be added or deleted as information becomes available.
• Hepatoprotective / Antioxidant / Berries: Study evaluated the hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of crude ethanolic extract of S. indicum berries in CCl4-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Results showed significant inhibitory activity on peroxides formation in linoleic acid emulsion in a dose-dependent manner. The hepatoprotective effect was attributed to its marked antioxidant activity from flavonoids with its free radical scavenging properties. (6)
• Anticonvulsant / Fruits: Study evaluated the anticonvulsant activity of methanol extracts of Crinum jagus and Solanum indicum bulbs and fruits, respectively, using mice and electroconvulsive shock equipment. C. jagus showed greater anticonvulsant effect. S. indicum showed activity at 112.50 mg/kg body weight. (7)
• Antitumor / Cytotoxicity on Seven Cancer Cell Lines: Study of whole plant yielded beta-sitosterol (1), beta-sitosterol glucoside (2), dioscin (3), methyl protoprosapogenin A of dioscin (5), methyl protodioscin (6) and protodioscin (7). Both CHCl3 soluble and insoluble fractions of ethanolic extract showed cytotoxicity on seven cancer cell lines: Colo-205 (colon), KB (nasopharynx), HeLa (uterine cervix), HA22T (hepatoma), Hep-2 (laryngeal epidermoid), H1477 (melanoma) and GBM8401/TSGH (glioma). (8)
• Cytotoxic / Solavetivone / Constituents: Study yielded solavetivone which was found to be cytotoxic to OVCAR-3 cells with an IC50 of 0.1 mM. Other compounds isolated were a novel solafuranone and three known compounds: scopoletin, N-(p-trans-coumaroyl)tyramine and N-trans-feruloyltyramine. (9)
• Antibacterial / Leaves: Ethanolic extract of leaves showed antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, E coli. A chloroform, acetone, and ethanol extracts showed activity against pseudomonas. (7)
• Anticariogenic / Flesh and Leaf: Dental plaque is a biofilm produced by cariogenic bacteria that attaches to the surface of teeth. Ethanolic extract from flesh and leaf of S. ferox has shown anticariogenic properties against S. pyogenes and S. aureus. The anticariogenic properties may be due to presence of phytochemicals such as alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins. (15)
• Indiosides / Anticancer: Studies have yielded several synthetic indiosides from S. indicum and shown to have anticancer effects. Results showed indiosides have a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on proliferation of Bel-7402 cells, and can induce apoptosis through mitochondria-dependent pathway. (16)
• Antibacterial / Fresh Leaves: Study evaluated the antibacterial potential of Solanaceae plants i.e., solanum indicum, S. xanthocarpum, and Physalis minima against selected pathogenic microorganisms. Ethanol and methanol extracts of fresh leaves of Solanum indicum showed moderate antibacterial activity against Bacillus spp., Corynebaterium diphtheriae, Streptococcus spp., Pseudomonas spp., and Salmonella typhimurium. (17)
• Cardiotonic / Laxative / Fruits: Study evaluated crude methanolic extract of fruits of Solanum indicum for laxative and cardiotonic activity in experimental animals. Results showed significant laxative activity (p value <0.01) and marked dose-dependent cardiotonic activity. (18)
• Anthelmintic / Fruits: Previous study reported on the strong anthelmintic activity of fruits of Solanum indicum. Study partially purified at least four different anthelmintic compounds. (19)
Toxicity Report
• Diabetes Insipidus: Study reports on a case of diabetes insipidus after seven doses of concentrated solution of Solanum indicum over two weeks. The diagnosis was confirmed by a water deprivation test and a low serum ADH. Results suggest that excessive doses of S indicum may cause central diabetes insipidus. (10)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Plants and seeds in the cybermarket.
|

![]()




 Botany
Botany Distribution
Distribution Uses
Uses