|
 Gen info Gen info
- Boehmeria is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Although related to the similar looking species of stinging nettles of the genus Urtica, the species of Boehmeria
do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are called "false nettles".
- Etymology: The genus name Boehmeria honors the German botanist Georg Rudolf Boehmer. (35) The specific epithet nivea derives from Latin niveus, meaning "of the snow or snowy" referring to the white underside of the leaves. (37)
•
The common name ramie derives from ramen, which the indigenous people of Sunda Islands (Indonesia) use to call the species. (36)
• Ancient use: The ancient use of ramie is evidenced by the clothes of Egyptian mummies, around 5000-3000 BC. It has been cultivated in China for many centuries. (36)
Botany
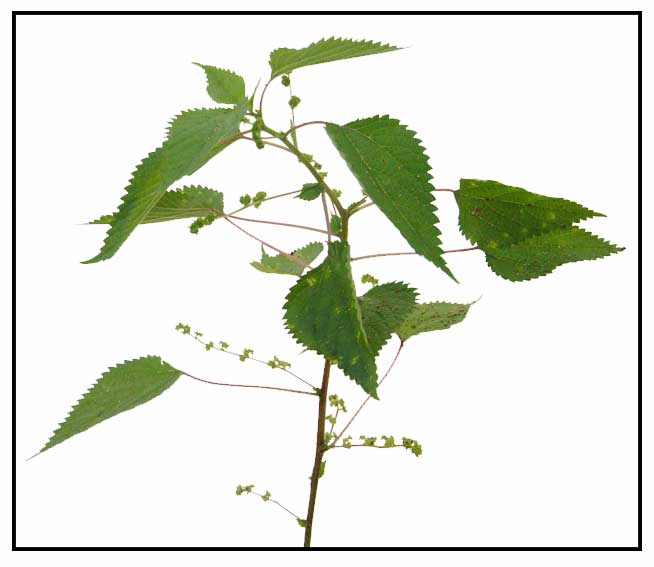
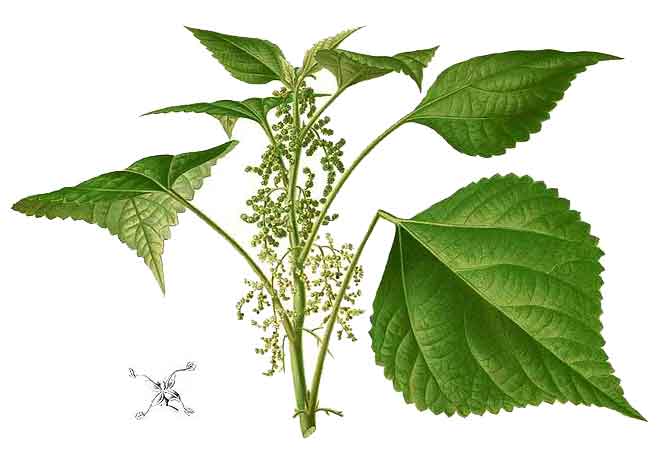
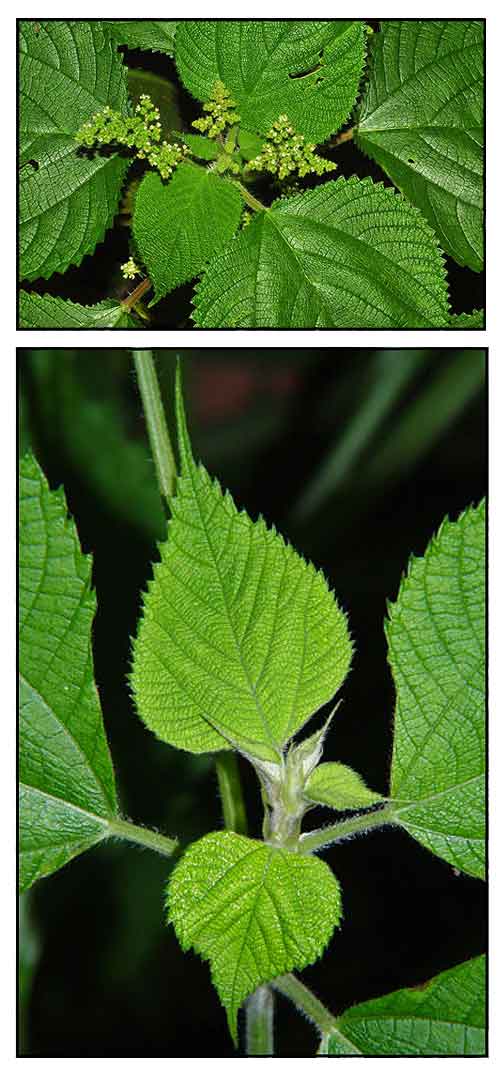
Ramie is an erect, branched,
monoecious perennial shrub, 1 to 2 meters high, with a single cylindrical
stem, and hairy branches and petioles. Leaves are long-petioled, alternate, broadly ovate, 10
to 18.5 centimeters long, 6 to 14 centimeters wide, with tapering pointed tip,
coarsely toothed margin, the upper surface green, roughened
with few scattered hairs, the lower surface white, except the
nerves, and densely covered with appressed, matted, white hairs. Flowers are small and clustered; the clusters arranged in
axillary panicles shorter than the petioles; unisexual, apetalous.
Staminate (male) flowers have 4 calyx lobes which are green in
color. Stamens are 4.
Distribution
-
Naturalized in Batan and Babuyan Islands.
-
Cultivated
in Mindanao and other parts of the Philippines for its fiber.
- Native to Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Cook Is., East Himalaya, Hainan, India, Japan, Kazan-retto, Korea, Laos, Myanmar, Nepal, Nicobar Is., Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam. (13)
- Now
cultivated in many tropical and subtropical countries.
 Constituents Constituents
- Bast contains lignin, 1.46%, and cellulose, 65.9%.
- Ash of leaves contains SiO2, 42.5%; CaO, 34.2%; K2O, 4.1%; NaO, 0.9%; MgO 6.5%; P2O5, 4.8%; SO3, 1.84%; Cl2, 1%.
- Leaves contain chlorogen acid.
- Study on chemical constituents of leaves yielded: kiwiionoside, eugenyl beta-rutinoside, uracil, beta-sitosterol glucoside, 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzoic acid, cholesterol, alpha-amyrin, and nonacosanol. (8)
- Study of roots yielded three compounds, viz. beta-sitosterol, daucosterol and 19-alpha-hydroxyursolic acid, obtained from the plant for the first time. (17)
- Leaves yielded flavonoids epicatechin, epicatechin gallate, and rutin. (see study below) (18)
- Study of leaves yielded eight compounds viz., kiwiionoside (1), eugenyl beta-rutinoside (2), uracil (3), beta-sitosterol glucoside (4), 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzoic acid (5), cholesterol (6), alpha-amyrin (7), and nonacosanol (8). (19)
- Study of leaves
yielded (-)-loliolide, rutin, ß-sitosterol, and pyrimidinedione. Loliolide was isolated for the first time. (20)
- Study of roots yielded
seven compounds: (1) p-hydroxybenzoic acid, (2) femlic acid, (3) protocatechuic acid, (4) pyrogallic acid, (5) 5-caffeoylquinic acid, (6) chlorogenic acid, and (7) caffeic acid. (see study below) (28)
Properties
- Mildly bitter and sweet tasting.
- Considered antipyretic, cooling, demulcent, diuretic, and resolvent.
- Like the common nettle of Europe, possesses styptic properties.
- Studies have suggested hepatoprotective, antioxidant, antiglycosidase, anticholinesterase, antidiabetic, phytoremediative, antihyperlipidemic properties.
Parts
utilized
Roots, stems and leaves
 Uses Uses
Edibility
· Leaves, roots, and seeds are edible.
· Use in preparation of tea.
· Green leaves are high nutritional elements: minerals, proteins, and vitamins.
Folkloric
· No known folkloric medicinal use in the Philippines.
· In China roots are reputed to be quieting to the uterus and recommended in threatened abortion.
· Pounded fresh leaves may be used as poultice for swelling pains
caused by sprains.
· Regulates placental movement,
hemostatic; for cold fever, urinary tract infection, nephritic edema,
edema among pregnant women, abnormal placental movements, and excessive
menstrual flow: 15.6 to 31 gms dried material in decoction.
· Used for wounds from poisoned arrows, for snake and insect bites.
· In decoction, used as local application in rectal disease.
· Leaves used in wounds and fluxes as astringent.
· Decoction of roots and leaves used as tonic in cases of dysentery.
· In Taiwan, used
in folk medicine for hepatoprotection and hepatitis treatment.
· Malays use the leaves for poulticing boils.
· Used for treatment of fluxes and wounds, prevent miscarriages
and promote drainage of pus.
· Malays use roots for treatment of foul ulceration (pekong) - fresh roots are mashed and used as poultice. Roots are also used as haemostatic, antiabortifacient and uterosedative; used for treatment of leukorrhea, vaginal bleeding, threatened abortion and for simple dysfunctional uterine bleeding, gaastrointestinal bleeding and piles. (23)
- Leaves are combined with roots and used as tonic for those suffering with dysentery. (23)
Others
• Fiber: A source of fiber or a constituent
of fabric with cotton, wool or silk. In the Philippines, the fiber is used for making strings, blankets, and cloth. It is one of the oldest textile
fibers, used in mummy cloths in Egypt around 5000-3300 BC. In terms of world trade, it is a minor crop.
• Ramie fabric: The natural fabric woven from the bast fiber of the ramie plant. It is also called China linen, grass linen, or grass cloth. It is much like flax, jute, or hemp in microscopic appearance. It is natural white in appearance, breathable, absorbent, six times as strong as cotton, twice as strong as flax, not itchy like linen, unaffected by light, rot, and insects. (33)
• Papermaking: Also used for production of papers, bank notes and cigarette
papers.
Studies
• Anti-Hepatitis
B: The study on the BN extract exhibited potential anti-HBV
activity in the animal model of HBV viremia. Â (1)BN extract significantly inhibited HBeAg and particle-associated HBV DNA secretion in an anti-HBV machinery different from the nucleoside analogues.
•Antioxidant / Hepatoprotective:
In a study of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury, results suggest the hepatoprotective and antioxidative effects of BN
probably involving mechanisms related to free radical scavenging. (2)
• Pollen-Induced
Bronchial Asthma: B nivea has been established to be a cause of asthma. The study showed no cross-reactivity with Parietaria and suggests that ramie may be a new independent allergen. (5)
• Toxicity Study / Embryonic Development: Commonly used to treat miscarriages, the test examined its safety for embryonic development in pregnant mice. Results showed B. nivea extract did not cause significant embyotoxicity or maternal toxicity in mice, although it caused cytotoxicity in cultured ECS (embryonic stem cells) at a high dose. (6)
• Free Radical Scavenging Activity: Study of ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of the root showed profound free radical scavenging activities.
• Antiglycosidase / Anticholinesterase / : Ethyl acetate extract showed maximum B-glucosidase inhibition. Leaf extract demonstrated the highest B-galactosidase inhibitory activity. The plant also exhibited notable BChE and moderate AChE inhibitory activity. Results suggest the whole plant provides strong biochemical rationale for the treatment of T2 diabetes, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. (7)
• Antidiabetic Potential / Glucose Uptake Stimulation: Study showed a reduction in high-fat diet increase in body weight, total cholesterol, and fatty liver, with improved fasting glucose level, blood insulin content, and glucose intolerance. (10)
• Phytoremediation / Cadmium: Ramie has great ability to tolerate and accumulate heavy metals. Study showed the feasibility of phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated farmland by ramie cultivars that have obtained cadmium accumulating capacity through screening and training. (11)
• GRP78 in inhibition of HBV secretion / Roots: Study of a root extract of B. nivea showed an inhibitory effect on blocking assembled virion secretion of HBV possibly through reduction of GRP78 (78-kDa glucose-regulated protein). (12)
• Antidiabetic / Antihyperlipidemic / Antioxidant / Roots: Study of evaluated an 80% methanolic extract of B. nivea root for antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects in STZ-induced diabetes in male Wistar rats. Results showed significant reduction in fasting blood glucose and total cholesterol together with increased HDL, liver glycogen content, superoxide dismutase, with reduced glutathione and catalase levels. (14)
• Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity / Leaves / Human HepG2 Cells: Study evaluated the anti-HBV effects of BNL extract in HepG2.2.15 cells transfected with human HBV DNA. Results showed reduction in the secretion of HBsAg and HBeAg in HepG2.2.15 cells. There was also a significant decrease in the content of HBV DNA in the medium secreted by the HepG2 cells. Among the fractions the CF and EAF exhibited the most potent anti-HBV activity. (15)
• Ramie Pollen Induced Asthma: Ramie has been established to be a cause of asthma. The rate of positive reactions to ramie in intradermal tests was 11.7% among adult asthmatic patients in the Nagasaki area. Ramie pollen-specific IgE antibodies were measured by ELISA, with the positive provocation test group showing higher O.D. values than the positive intradermal test group (p < 0.05). In cross-reactivity study, results ramie may be a new independent allergen. (16)
• Flavonoids / Leaves: Study evaluated the flavonoid content of leaves of Boehmeria nivea. The content of epicatechin, epicatechin gallate, and rutin was highest in the leaves. In commercial products, epicatechin and epicatechin gallate was highest in ramie tea. (18)
•
Free Radical Scavenging / ACE Inhibitory / Anticancer / Leaves: Study evaluated the antioxidant activity, angiotensin 1-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity and anticancer activity of Boehmeria nivea leaves. An ethyl acetate fraction (EF) showed strong DPPH radical scavenging activity, superoxide radical scavenging activity and hydroxyl radical scavenging. The EF showed ACE-inhibitory activity of 80.32% at 0.1 mg/mL and growth inhibitory effect on LoVo cell line and NCI-H460 cells line. (21)
• Neuroprotective / Protective Effects Against Oxidative Stress in C6 Glial Cells: Study evaluated 9 kinds of ramie for protective action against oxidative stress in a cellular system of C6 glial cells. Treatment with H2O2 and Aß25-35 induced loss of cell viability and high levels of ROS generation. Treatment with B. nivea led to increase in cell viability and decrease in ROS production. Results suggest excellent anti-oxidative properties and potential for prevention of neurodegeneration by reducing oxidative stress in cells. (22)
• Invention / Treatment of Liver Fibrosis: Study describes a method for treating liver fibrosis which involves administering a pharmaceutically active extract obtained from a Boehmeria species (B. nivea or B. frutescens). Study also describes a method for regenerating liver tissue and method for improving liver function. (24)
• Diseases of Ramie: Ramie, the vegetable fiber, is obtained from the stem of B. nivea (L.) Gaud. and is used in many textile products. Study reports on the diseases of ramie, its occurrence, symptoms, and control measures. The major and most widespread diseases are: (1) white fungus caused by Rosellina necatrix, (2) leaf spot caused by Cercosporo spp. and Phyllosticta spp., (3) seeding rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani, (4) cane rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina, and (5) eye rot caused by Myrothecium roridum. (25)
• Novel Suture Biomaterial:From natural origin, only silk, cotton, and linen fibers are available as non-absorbably suture biomaterials. This study reports on a novel, cost-effective, and biocompatible suture biomaterial from ramie plant. Results report on the physiochemical properties of raw and degummed ramie fiber, where the former showed desirable characteristics for suture preparation. Braided multifilament ramie suture from degummed fiber showed excellent tensile strength. The suture was found to be biocompatible towards human erythrocytes and nontoxic to mammalian cells. The suture exhibited significant antibacterial activity against E. coli, B. subtilis, and S. aureus, probably from inherent bacteriostatic ability of the plant fiber. Study suggests tremendous possibility for utilization of the ramie plant for various biomedical applications. (27)
• Antioxidant Activity / Roots: Study of roots yielded
seven compounds: (1) p-hydroxybenzoic acid, (2) femlic acid, (3) protocatechuic acid, (4) pyrogallic acid, (5) 5-caffeoylquinic acid, (6) chlorogenic acid, and (7) caffeic acid. Screening for antioxidant activity yielded IC50 values of 32, 57, 38, 54, 39, 76, and 58µg/mL, respectively. (28)
• Mechanical Properties of Ramie Reinforced Polymer Composite: Study reports on the feasibility of polymer matrix composites= of ramie fiber collected from the plant bark of B. nivea. This study analyzed the tensile strength, compression and pleural properties of B. nivea (7% of fiber by weight) reinforced polymer matrix composites. (29)
• Improvement of Yield and Fiber Firmness: Study suggested that for soils similar to Maahas clay loam, the application of ramie wastes plus addition of 45-30-30 kg/ha of N, P2O5 and K2O and harvesting of 40 DAR would produce a respectable dry fiber yield with acceptable fiber firmness. (30)
• Inhibition of Tumor Cell Growth and Drug Resistance: Prostaglandins are formed by arachidonic acid through activities of cyclooxygenases (COX 1 and 2) and subsequent downstream enzymes. Study found that BNE-101 (B. nivea extract) has potential in regulating P-gp protein expression levels and reducing drug resistance in cancer cells. BNE-101 could decrease inflammation, inhibit cancer cell growth and reduce P-gp protein mediated multidrug resistance (MDR). Results suggest potential in prevention and treatment of cancer. (31)
• Decreased Cholesterol in Ovariectomized Rats: Dyslipidemia is a major cause of morbidity, mortality, and high cost of treatment. The decrease of estrogen production during menopause periods are associated with higher risks of dyslipidemia and coronary heart disease. This study reports on the ability of ethanolic root extract to increase uterine weight and improve dyslipidemia on ovariectomized mice. The phytoestrogenic effects of B. nivea was probably contributed to by isoflavone and lignan compounds. (32)
• Laxative / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study evaluated the protective effects of ramie leaf ethanol extract (RLE) against loperamide-induced constipation and oxidative stress in male Sprague-Dawley rats using doses of 200 or 400 mg/kbw by gavage. Results showed decrease in total fecal number, wet weight, and water content, while total number of loperamide-induced fecal pellets in the distal colon increased in a dose-dependent manner. Gastrointestinal transit time was greatly reduced, along with significantly lower total cholesterol, ALT, and ALP. There was also dose-dependent decrease in intestinal mucosal malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). While loperamide decreased antioxidant activity, including SOD and GSH-Px, RLE increased antioxidant activity. Results suggest potent laxative and antioxidant effects in the rat model of loperamide-induced constipation. (34)
Availability
Wild-crafted. |



