| 
Gen info
- Codiaeum variegatum is a species of plant in the genus Codiaeum, a member of the family Euphorbiaceae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
- There are several hundred cultivars, selected and bred for their foliage. (37)
- 'Garden croton' is a common name, but it should not be confused with Croton, a cosmopolitan genus also in the Euphorbiaceae family, which contains more than 70 species of herbs, shrubs, and trees. (37)
Botany
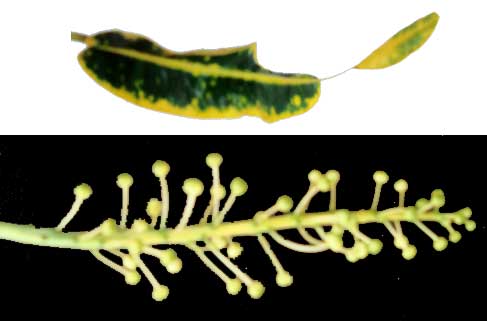
Sagilala is a low branching shrub with attractive
and variedly shaped and colored foliage. Leaves are thick and leathery,
ovate, oblong to linear, the margins entire, lobed or spirally twisted.
Young leaves are usually green, yellow or red, later changing to single
color or variegation of gold cream, white, red, maroon, purple, black
or brown. A milky sap bleeds from cut stems. Flowers are small, long, axillary, usually unisexual racemes.
 Distribution Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
- Also native to Bismark Archipelago, Borneo, Fiji, Jawa, Lesser Sunda Is., Maluku, New Guinea, Queensland, Santa Cruz Isl, Solomon Is., Sulawesi, Vanuatu.
(28)
-
A very popular cultivated ornamental
in the Philippines.
- Probably native to the Moluccas.
- Cultivated in most tropical countries.
Constituents
• Studies have yielded alkaloids, terpenes, flavonoids.
• Study of six clone cultivars of Codiaeum
variegatum showed the shoots to be rich in alkaloids (most abundant),
cardiac glycosides, saponins, tannins, cardenolides, steroids and phyllates.
• Phytochemical screening of the plant yielded saponins, reducing sugars, tannins, and gums.
• Study of extracts of leaves from two varieties of CV (spiral/CP and royal like/BP) yielded (-)-Epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, rutin hydrate and ellagic acid. (see study below) (16)
• Phytochemical screening of various solvents of root, leaf, and stem yielded alkaloids (4.66 - 10.2%), carbohydrates, glycosides, steroids, flavonoids (33.1 -37.63%), coumarins, saponins (11.36 - 13.76%), fatty acids, tannins (10.5 - 18.5%), proteins and amino acids, gum and mucilage, terpenoids (27.56 - 30.3%), anthroquinones and phenols (33.43 - 39.76%). (29)
- Study of methanolic extract of C. variegatum cv. spirale yielded five flavonoids i.e., apigenin, vitexin, isovitexin, and vicenin-2 along with phenolic acids, caffeic and p-coumaric acids.
(see study below) (33)
Properties
• Leaves are considered purgative,
sedative, antifungal, antiamoebic, antioxidant, and anticancerous.
• Considered emmenagogue and abortifacient.
• Studies have suggested antioxidant, antifertility, molluscicidal,immunomodulating, cytotoxic, wound healing, antimicrobial, antiamoebic, antilithiatic and anticonvulsant properties.

Parts utilized
Leaves, roots, bark.
Uses
Edibility
- Caution: Young leaves are reportedly used in the East Indies as vegetable, but cases of irritation have been reported. (See toxicity below)
 Folkloric Folkloric
- Freeze-dried leaf decoction taken
as tea in the Philippines (Gertrudes, 2006).
- Decoction of crushed leaves for diarrhea.
- Young leaves, with Pandanus macroieacceretia, coconut milk, and root
sap of areca catechu used for gonorrhea.
- Sap of leaves mixed with coconut milk used for syphilitic lesions.
- In Nigeria, root decoction
used for gastric ulcers. Leaves, for antibacterial and antiamoebic uses.
- In the Kagera and Coast
regions, used for the treatment of epilepsy.
- In Cameroon, leaves used for bloody diarrhea.
. In Indonesia, leaves used for the treatment of eczema.
- In Vanuatu, leaves used for amenorrhea. Chewing of 3 leaves and
swallowing the juice used as emmenagogue, to induce abortion or facilitate
parturition. (8)
- In Bangladesh, used by the Marma healers for fevers, cough, and colds. (23) In Unani practice, leaf juice is boiled with fruit oil of Olea europaea and massaged on painful areas. (25)
- In New Guinea and the Solomon Islands, used as abortifacient; leaves chewed and swallowed as contraceptive. In the North Solomons Province, the crushed root is mixed with sulfur and the mixture chewed to induced sterility. In Malaysia, a hot water extract is used to cause abortion. (27)
- In the Fijian Islands, bark decoction used to treat eczema, psoriasis, and allergies. Leaves also used to treat fish poisoning and gonorrhea. (28)
- In New Guinea, croton root is chewed with betel nut to treat stomachache or applied to affected area to relieve toothache. A green bath prepared from boiled
leaves used for fever. Sap squeezed from leaves or incised from bark applied to sores and fungal infections. Drink prepared from leaf sap given for snake bites and applied to the affected bite area. Decoction of entire plant used to induce abortion. A mixture of crushed root mixed, volcanic sulphur and betel nut is chewed to induced sterility in women. Infusion of scraped barks of croton and Albizzia falcataria drunk for patients suffering with rectal prolapse. (34)
Studies
• Phytochemicals: Phytochemical screening of six clone cultivars
of Codiaeum variegatum showed bioactive constituents that included alkaloids,
anthraquinones, flavanoids, terpenes, steroid, phenol, saponins, tannins,
phlobatannin and cardenolide which suggests their use as antibacterial,
antiamoebic and antifungal. (2)
• Antiamoebic: Study evaluated 55 traditional medicinal plants in Cameroon for amoebicidal activities. using a polyxenic culture of Entamoeba histolytica. Of 14 extracts that exhibited antiamoebic activity on initial screening, only the leaves
extract of Codiaeum variegatum exhibited clear antiamoebic activity (EC50=10.74 on the second day),
with a more pronounced activity than reference metronidazole. (3)
• Anti-influenza:
A screening of seven Euphorbiaceae species showed C variegatum to be
one of three with relevant anti-FLUAV activity from an isolated cyanoglucoside. (4)
• Anti-convulsant / Leaves:
Study evaluated aqueous and methanol extracts of inhibitory effect on picrotoxin-induced convulsions in adult Theiller's while albino mice. A methanol extract showed significant (P<0.05) protection of mice against picrotoxin-induced convulsions via oral and i.p. routes. (5)
• Immunostimulating / Spermatotoxic:
Study on 24 male albino rats with feeds supplemented by pulverized dry leaves of C variegatum showed immunostimulating and spermatotoxic effects. (6)
• Molluscicidal Activity:
Study showed the latex of Codiaeum variegatum had high molluscicidal activity against freshwater snail. (7)
• Wound Healing / Root: Study evaluated the wound healing activity of a root incorporated in a simple ointment in excision, incision, and burn wound models in rats. Results showed remarkable wound healing activity in measures of wound contracting ability, wound closure time, and tensile strength. (11)
• Antimicrobial Activity: Study evaluated the antibacterial activity of three varieties of Codiaeum variegatum against six different bacterial strains. Zones of inhibition varied with the plant varieties. The largest zone of inhibition was seen with a leaf callus extract of var. Punctatum aureum against Arthrobacter. (14)
• Cytotoxicity: Phytochemical screening yielded the presence of saponins, reducing sugars, tannins, and gums. Brine shrimp lethality bioassay indicates that the plant has cytotoxic properties. (15) In a study of 61 medicinal plants of Malaysia for cytotoxicity against HeLa cell line, Codiaenum variegatum was one of 18 plants that showed cytotoxic activity. (26)
• Antioxidant / Phenolic Content: Study evaluated in vitro antioxidant potential of two varieties of C. variegatum leaves using various assays. Extracts showed effective DPPH radical scavenging, hydrogen peroxide radical scavenging, and NO scavenging activity. Extracts yielded (-)-epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, rutin hydrate and ellagic acid. Results showed CV leaves contain high amount of phenolic compounds which may be responsible for its biologic activities in folkloric medicine. (16)
• Anti-Amoebic / Entamoeba histolytica: Study searched for active components from C. variegatum against Entamoeba histolytica and their mechanism of action. Subfractions were identified with significantly higher anti-amoebic activity. Results suggest regulation of ceramide biosynthesis pathway as a target for anti-amoebic compounds could be an alternative for drug development against E. histolytica. (17)
• Antibacterial / Fresh Leaves: Study evaluated the antibacterial activity of extract of fresh leaves against four test microorganisms, viz. E. coli, P. aeruginosa, B. subtilis and S. aureus. (19)
• Antiviral / Cytotoxicity: In a study evaluating some plants used in Malaysian indigenous medicine, C. variegatum showed activity against VSV (vesicular stomatitis viruses) and cytotoxicity using the HeLa cell line assay. (20)
• Larvicidal / Culex quinquefasciatus: Study evaluated five species of Philippine plants for larvicidal potential against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Codiaeum variegatum showed to be the third most potent larvicide against Culex quinquefasciatus. The leaves have previously shown molluscicidal properties against Oncomelania hypensis quadrasi (Garcia, 1990) which suggests an inherent pesticidal component in the leaves. (22)
• Genotoxic and Mutagenic Testing of Extract and Amoebicidal Fraction:Study evaluated the genotoxic and mutagenic potential of an aqueous extract and isolated sub-fraction. Results showed the aqueous extract of CV and the amoebicidal fraction SF9B are neither genotoxic on non-competent or metabolic competent cell lines, nor mutagenic in mouse lymphoma mutation assay and therefore can be safely used at lower doses for medicinal purpose. (24)
• Cytotoxicity / Human Leukemic, Breast, and Prostate Cancer Cell Lines: Study evaluated crude extracts and fractions of stem bark and leaf for cytotoxic activity against human leukemic, breast and prostate cancer cell lines. Both crude extracts showed antiproliferative activity towards all cancer cell lines, with the stem bark showing strongest cytotoxicity. Mechanism of cell death was attributed to apoptosis. On further testing, a chloroform fraction of crude extract of stem bark showed increase cytotoxicity against Jurkat cells with IC50 of 44.71 ± 0.44 µg/mL. (30)
• Antilithiatic: In-vitro study of an ethanolic extract of Codiaeum variegatum showed antilithiatic activity in a synthetic urine preparation. (31)
• Histological Effects on Rat Cerebrum / Leaves: Study of ethanolic leaf extract
showed adverse effect on the cerebrum of adult Wistar rats as evidenced by sparse cellular population migroglial infiltration, focal and liquefactive necrosis when compared to the control group. (32)
• Phenolic Compounds / Vitexin, Isovitexin, Apigenin / Antioxidant Activity: Study evaluated the antioxidant activity of compounds isolated from a methanol extract of C. variegatum cv. spirale. Vitexin exhibited highest DPPH radical scavenging antioxidant activity (IC50=8.95 µg/ml). Vitexin and isovitexin showed significant reducing power (RP50=8.65 and 9.27 µg/ml, respectively). Apigenin showed highest activity against lipid peroxidation (IC50=31.82 µg/ml). (see constituents above) (33)
• Tumor Promoting Activity: A 1995 study screened 48 species of Euphorbiaceae with an in vitro assay using a human lymphoblastoid cell line harboring the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) genome. Twenty-seven percent (13/48) were found positive, and four species, including Codiaeum variegatum, exhibited EBV-inducing activity. Study suggests caution for the regular users of these plants because of its tumor-promoting activity. (36)
• Antipyretic / Leaves: Study evaluated an ethanol fraction of leaf extract for antipyretic activity in male mice with fever was induced by DPT-HB-HIB vaccine. The extract at dose of 143 and 286 mg/kbw showed antipyretic effect, statistically similar to paracetamol. (38)
• Protective Against Genotoxicity Induced by Carmustine / Leaves: Carmustine (Cr) is a chemotherapeutic drug used in the treatment of brain tumors. Study evaluated the protective role of C. variegatum leaves ethyl acetate fraction against genotoxicity of Cr. Cr induced significant increase in MPCEs and chromosomal aberrations (CAs) in the bone marrow, induced significant percentage of CA in spermatocytes in meiosis, and significant morphological sperm abnormalities. C. variegatum mitigated all deleterious genotoxic effects of Cr. Chemical analysis showed flavones (35.21%) and phenolic acids (17.62%) as main components. (39)
• Antidiarrheal / Tannin Content / Leaves: Study evaluated the antidiarrheal activity using castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice and total tannin content of ethanolic extract of leaves of Codiaeum variegatum.
Results showed a positive anti-diarrheal effect with inhibition of mean number of defecation by 40.81% and 59.18% (p<0.01 and p<0.001) at 250 and 500 mg/kbw, respectively, along with increase in latent period in the extract group. The total tannin content was significant and high (241.41 mg/g of tannic acid equivalent). Phytochemical screening of leaf extract yielded carbohydrate (reducing sugars), gums, steroids, alkaloids, and tannins. (40)
Toxicity
!
• Chewing on the bark and roots can cause burning
around and in the mouth. Some leaves are reported irritant. Latex have
been reported to cause eczema.
• There has been a report of occupational contact dermatitis.
• Report of Contact Dermatitis: Study reports on a case of contact eczema in a nursery gardener. Patch tests with Croton leaves were positive. Results suggest: (1) the latex produces no primary irritant reaction, (2) the latex can induce contact allergy, and (3) contact allergens are constituent of the milky sap. Sensitization experiments in guinea pigs with methanolic extract of leaves were successful. (21)
- Toxicity is attributed to chemical compound 5-desoxyingenol. The plant also contains an oil that is violently purgative, and suspected of being a carcinogen. Consumption of the seeds has been reported fatal to children.
(37)
Availability
Cultivated.
|



 Distribution
Distribution
 Folkloric
Folkloric


